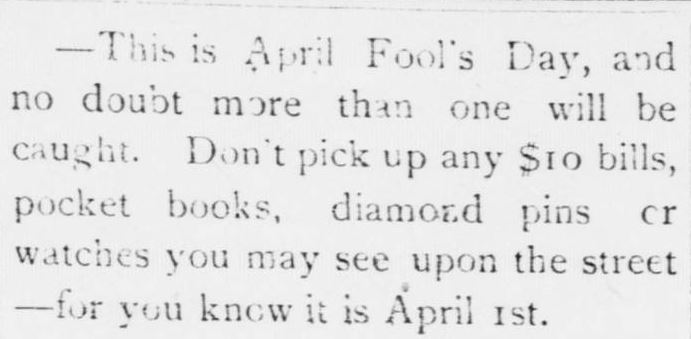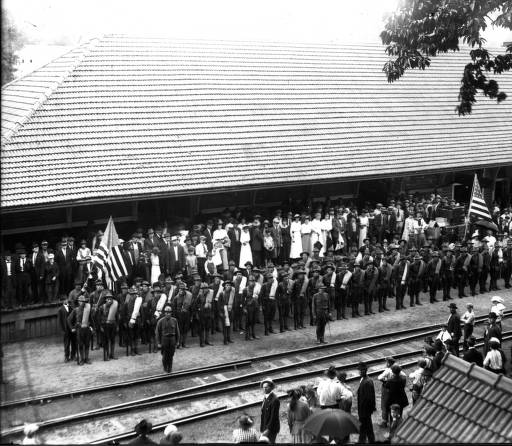
Company H, WWI, 1st North Carolina Infantry of the National Guard, departed Waynesville’s train depot on June 26, 1916. They guarded the Mexican border and returned to Waynesville in February 1917. In July 1917 they then were sent to France during WWI. Courtesy of Haywood County Public Library.
Last Thursday, April 6, 2017, marked the 100th anniversary of the United States’ entry into World War I. Over the next year, many cultural heritage institutions around the country are highlighting the materials they hold related to the “Great War.” We wanted to highlight some of the fantastic local North Carolina materials we have digitized for our partners that document the World War I perspective from North Carolinians’ eyes.


Service records, photographs, news clippings and letters back home from communities across the state are digitized here on DigitalNC. From Wilson County, we have a set of records from 70 men that served in the war that the United Daughters of the Confederacy collected and a scrapbook that includes letters from a Robert Anderson before he was wounded in action and died in France. From Stanly County, we have an enlistment record that includes the amount Harvey Jarvis Underwood was paid to serve, and a history of the service records of Stanly County men who served in the war. From the Grand Lodge of the Ancient, Free, and Accepted Masons of North Carolina, the NCDHC digitized a list of all the North Carolina masons who died in World War I.

Several scrapbooks from Elon University detail the students’ view of the war as well as what college life during World War I looked like here in North Carolina.

Headline from Page 2 of the April 12, 1917 edition of the Roanoke News

The richest source of information on World War I and North Carolina on DigitalNC may very well be the many local newspapers we’ve digitized that contain the local perspective on the war, including some quite subdued headlines announcing the US’s entry. DigitalNC also hosts several World War I camp and hospital newspapers including the Trench and Camp from Camp Greene and the Caduceus, the paper of the Base Hospital at Camp Greene. Both are from Charlotte Mecklenburg Library.
To view more materials from World War I, check out a search of our collections here. And to learn more about World War I materials from across the state, visit the institutions highlighted in this blog post from our colleagues over at the State Archives of North Carolina.
Mascots are a complicated phenomenon. They inspire a spectrum of reactions: ridicule, ambivalence, or fierce loyalty. With thousands of yearbooks online, all of us here at the Digital Heritage Center have probably spent more time looking at yearbooks than anyone else you’re likely to meet. Mascots are a common theme.
I’ve been working on today’s post for quite some time; unable to find a history or comprehensive list of mascots in North Carolina I decided to compile one myself. So here’s a stab at a college mascot overview, drawn from yearbooks and other campus publications. Let me know what I’ve missed or gotten wrong!
Children
In the early 20th century, schools frequently chose children as mascots or sponsors, whether for a sports team or for a particular class. The earliest example we’ve found on DigitalNC is from a 1910 publication by Atlantic Christian College (now Barton College) in Wilson, which shows Elizabeth Settle Caldwell as the Senior Class sponsor.

Elizabeth Settle Caldwell, First North Carolina Mascot? From the 1910 Pine Knot yearbook, Atlantic Christian College.
Ms. Caldwell was the daughter of Jesse Cobb Caldwell, the college president. From what we’ve been able to tell, children mascots were frequently younger siblings of students, teachers, or others associated with the school. Students mention that Ms. Caldwell brought “solace to many a lonely, homesick heart” and this may be why children were chosen – to foster a feeling of family and comfort among students. We’ve seen several references to mascots being elected or being chosen through competition, although what this might be we haven’t been able to discover. The trend of choosing children as mascots seems to continue through the 1960s. The latest one we found is Dawn, the Senior Class mascot at Peace College (now William Peace University) in 1966.
Animals
Animal mascots span schools across the state, whether it’s Rameses at UNC-Chapel Hill or WCU’s Catamount. The bulldog and different types of cats win out as most frequently adopted. Pictures of live animal mascots start to appear in yearbooks in the early 1900s, and continue today although much less frequently. For a variety of reasons, including concerns expressed by animal rights activists, schools have shifted away from actual animals to students dressing up like animals, as you’ll see later on in this post.
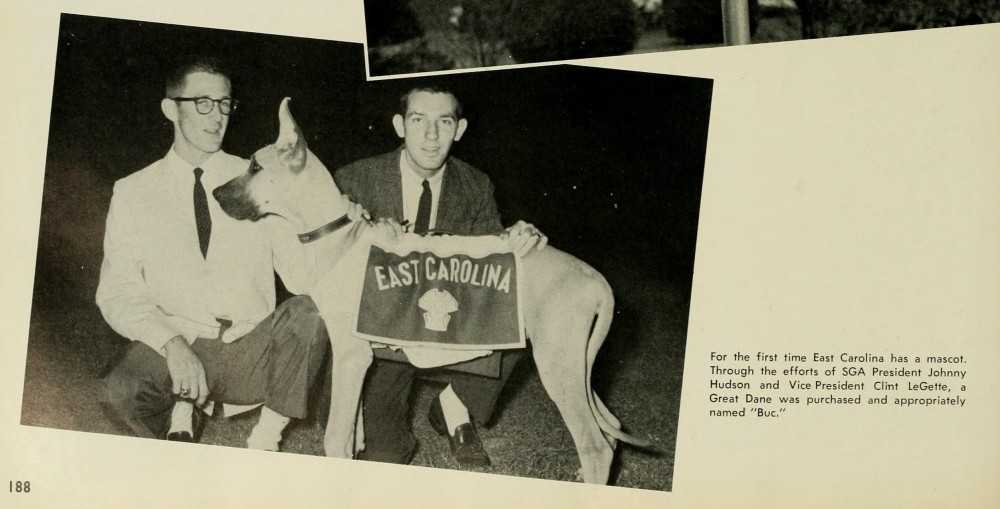

“Buc” is described here as East Carolina University’s first mascot. From the 1959 Buccaneer yearbook.
Characters
While about half of the four-year college mascots in North Carolina are animals, most of the others are characters that are historic, mythical, or extraordinary in nature. From what I’ve seen in NC yearbooks, humans dressing up as the school mascot really got traction in the 1960s. Initially, these costumes weren’t the fuzzy creations we think of today, but rather less complicated ensembles where the mascot’s identity (his or her face and body) was often apparent. Yosef the Mountaineer, beloved icon of Appalachian State University, was created sometime around 1942 and looked like this in the 1960s:
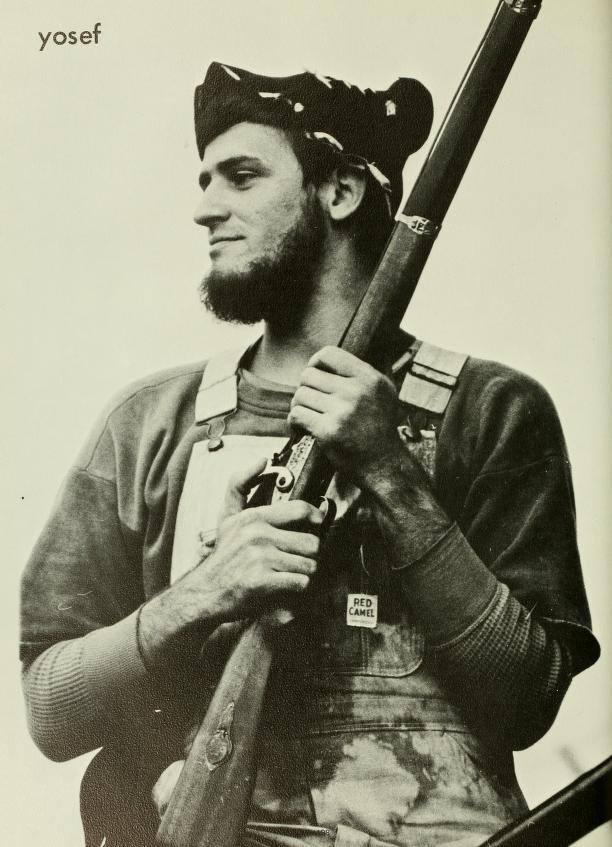

Yosef the Mountaineer, aka James Randle Tedder (we think). From the 1969 Rhododendron yearbook, Appalachian State University.
One of my favorites has to be this picture of Duke Blue Devil, from 1950:
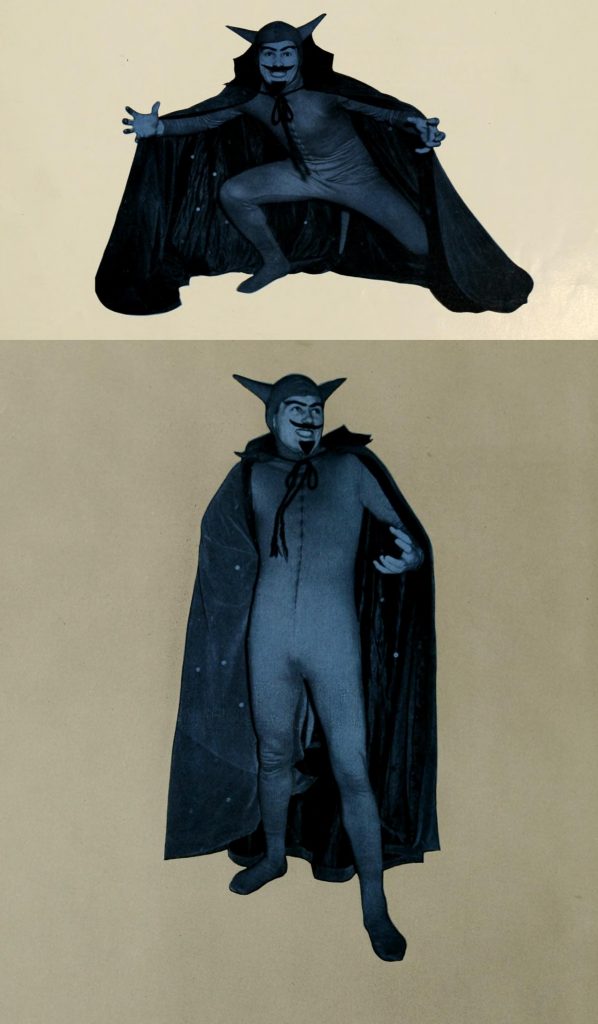

The Blue Devil. From the 1950 Chanticleer yearbook, Duke University.
Perhaps it was too hard to maintain a degree of consistency as students graduated over the years, and mascot anonymity seemed like a better idea. Whatever the reason, you start to see fuzzy, oversized costumes with gigantic headpieces in the late 1970s.
The Big Costumes
Whether animal or character, plush mascots that include a single piece body suit with a large plastic or cloth-covered head is something most Americans can identify with, thanks to professional sports. Colleges in North Carolina really embraced these costumes through the 1980s. Here’s what the UNC-Wilmington Seahawk looked like in 1987:

The Seahawk. From the 1987 Fledgling yearbook, UNC-Wilmington.
Some schools have developed multiple mascots dedicated to different audiences. It seems like the difficulty with these types of costumes is how to pull off a fierce facial expression that doesn’t come off as goofy or too scary for children. I think this picture from Davidson College sums it all up:

The Davidson Wildcat and … friends. From the 1983 Quips and Cranks yearbook.
I will also take this opportunity to mention a mascot that routinely makes the “wait … what?” list – the Campbell University Fighting Camels:
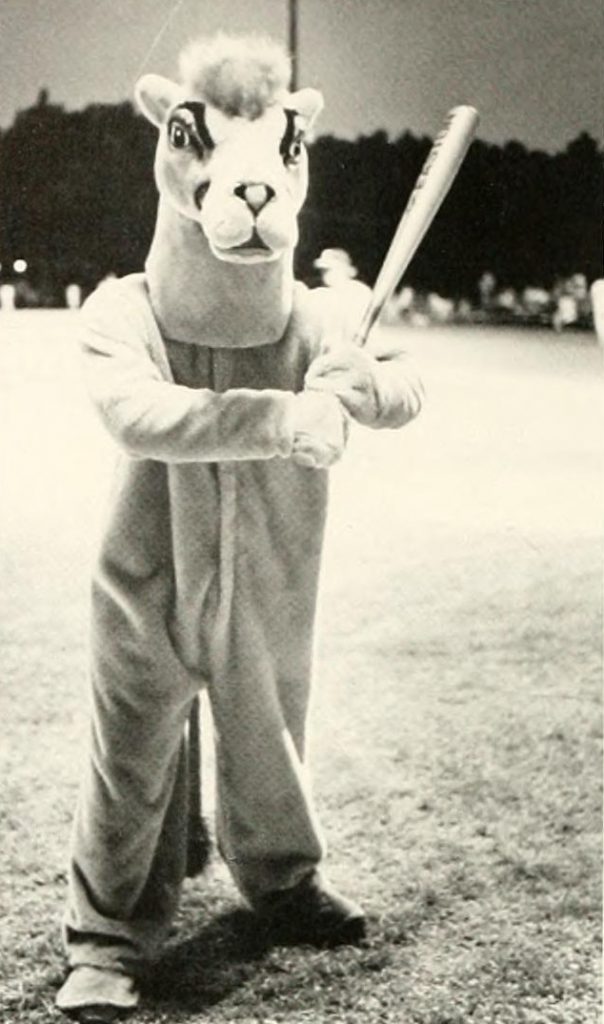

The Campbell Camel. From the 1983 Pine Burr yearbook.
Even the humans and human-like creatures are clothed in oversized costumes these days. Wake Forest University’s Deacon is a dapper chap:
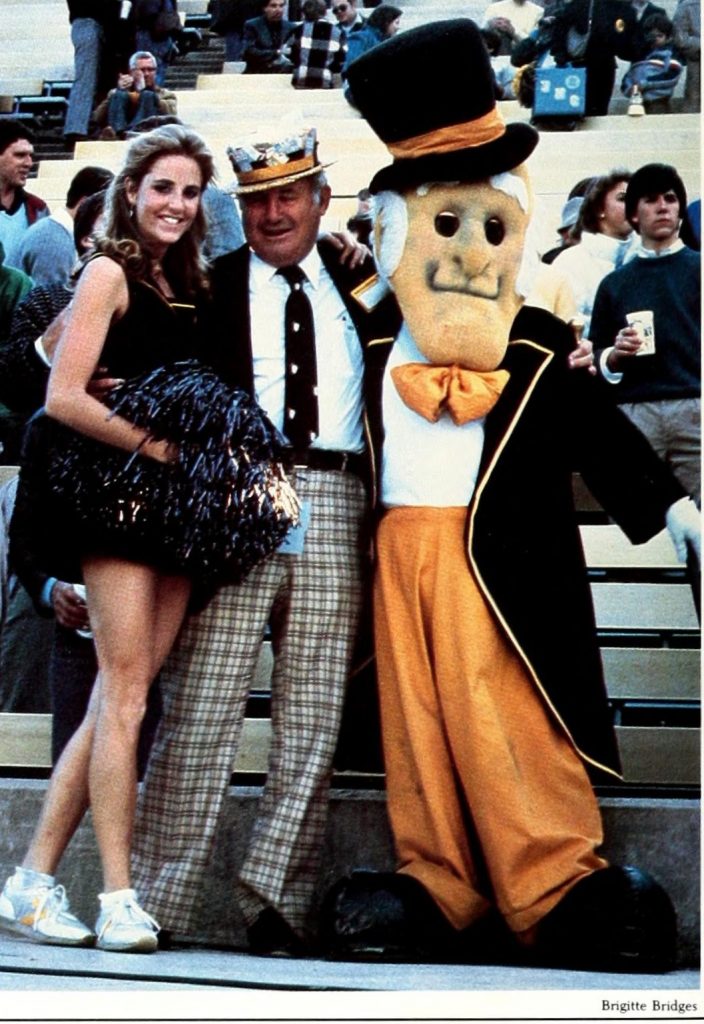

Wake Forest’s Deacon poses with fans. From the 1985 Howler yearbook.
In addition to the Demon Deacons and the Blue Devils, North Carolina boasts a number of other spiritual mascots: North Carolina Wesleyan’s Battling Bishops, Belmont Abbey’s Crusaders, and Guilford College’s Quakers. Meredith College’s teams are known as the Avenging Angels (formerly just the Angels). While Elon University’s mascot is now the Phoenix, before 2000 they were the Fighting Christians:
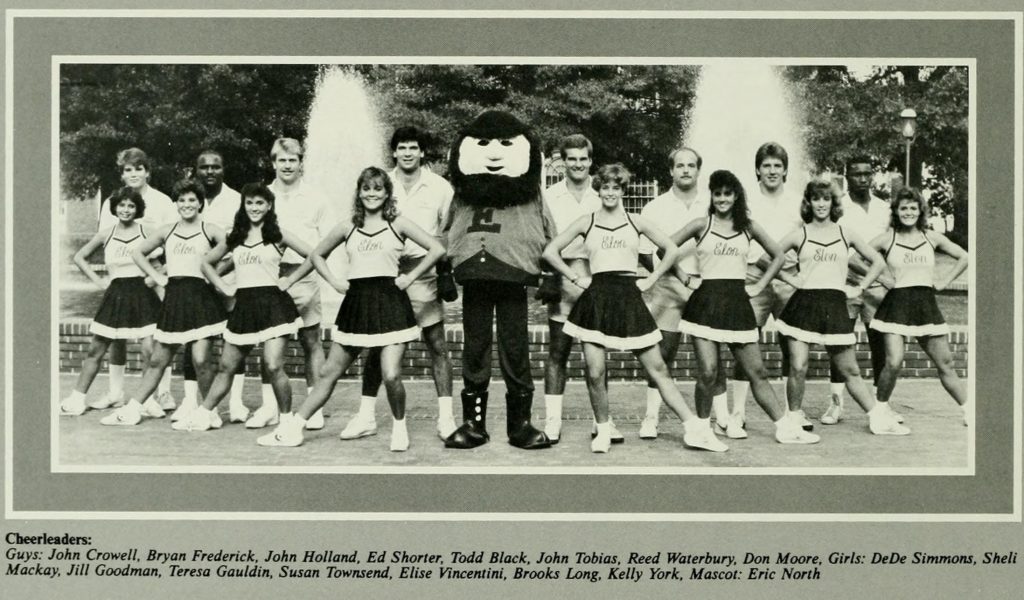

The Elon Fighting Christian mascot with cheerleaders. From the 1986 Phi Psi Cli yearbook.
Two schools break with the animal/human tradition in North Carolina. The Brevard College Tornadoes and the Louisburg College Hurricanes. Weather phenomena mascots are always difficult to pull off. I couldn’t find one for Brevard, but Louisburg, which currently has a bird mascot, had “Louie” up until 2006:
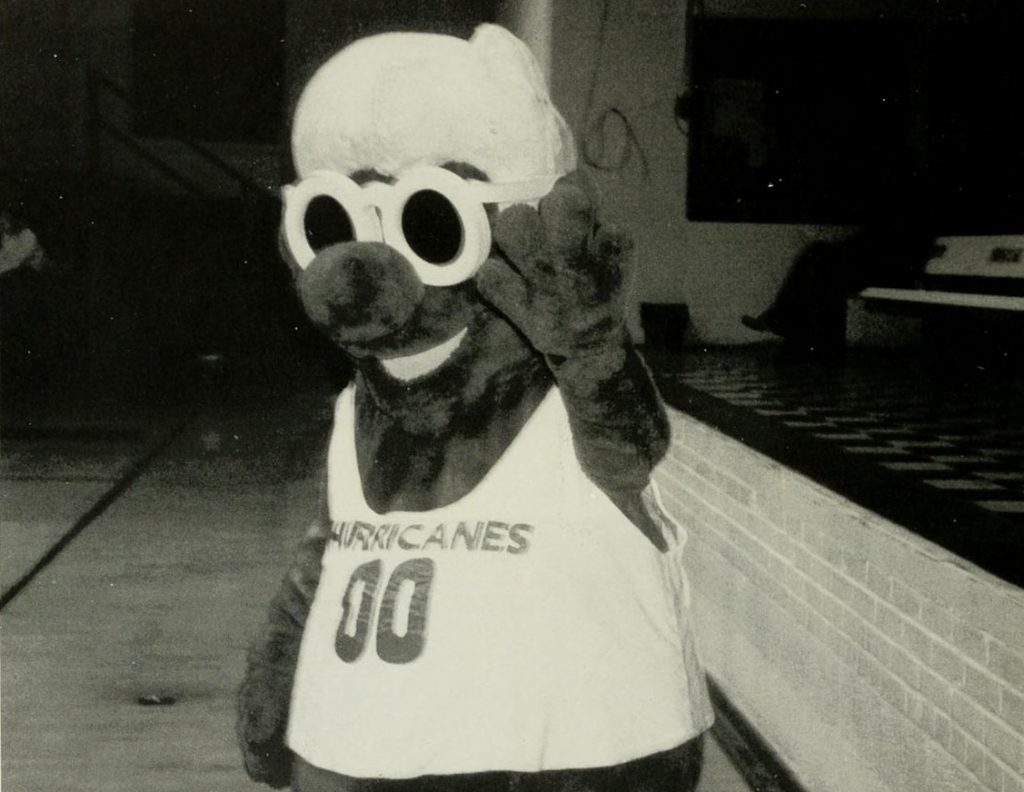

Louie, the former Louisburg College Hurricanes mascot. From the 1996 The Oak yearbook.
Who knows when the next mascot sea change will happen. Below is a list of mascots in North Carolina; let us know if we got anything wrong. Which one is your favorite?
| School |
Mascot |
Notes |
| Appalachian State University |
Yosef the Mountaineer |
First appeared in the yearbook in 1942 |
| Barton College |
Bulldog |
|
| Belmont Abbey College |
Crusader |
|
| Bennett College |
|
Known as the Bennett Belles |
| Brevard College |
Tornado |
|
| Campbell University |
Fighting Camels |
The Hornets in the 1920s-1930s |
| Catawba College |
Catawba Indian |
|
| Chowan University |
Hawks |
The Braves until 2006 |
| Davidson College |
Wildcats |
Also a bulldog (1929) and a bobcat (1939) |
| Duke University |
Blue Devil |
|
| East Carolina University |
Pirates |
Formerly Pee Dee the Pirate |
| Elizabeth City State University |
Vikings |
|
| Elon University |
Phoenix |
The Fightin’ Christians until 2000 |
| Fayetteville State University |
Broncos |
|
| Gardner-Webb University |
Runnin’ Bulldogs |
|
| Greensboro College |
The Pride |
Formerly the Hornets |
| Guilford College |
Quakers |
|
| High Point University |
Panthers |
|
| Johnson C. Smith University |
Golden Bulls |
|
| Lees-McRae College |
Wily the Bobcat |
|
| Lenoir-Rhyne University |
Joe and Josie Bear |
|
| Louisburg College |
Hurricanes |
|
| Mars Hill College |
Mountain Lion |
|
| Meredith College |
Avenging Angels |
Formerly the Angels |
| Methodist University |
Eagles |
|
| Montreat College |
Cavaliers |
|
| Mount Olive College |
Trojans |
|
| North Carolina A&T |
Aggie Dog (Bulldog) |
|
| North Carolina Central University |
Eagles |
|
| North Carolina State University |
Wolfpack |
|
| North Carolina Wesleyan College |
Battling Bishops |
Formerly the Circuit Riders |
| Peace College |
Pacer |
|
| Pfeiffer University |
Falcons |
|
| Queens University of Charlotte |
Rex the Royal |
|
| Saint Augustine’s University |
Mighty Falcons |
|
| Salem College |
Spirits |
|
| Shaw University |
Bears |
|
| St. Andrews University |
Knights |
|
| UNC Asheville |
Bulldog |
|
| UNC Chapel Hill |
Rameses the Ram |
Also known as the Tar Heels |
| UNC Charlotte |
Norm the Niner |
|
| UNC Greensboro |
Spartans |
|
| UNC Pembroke |
Braves |
|
| UNC Wilmington |
Seahawk |
|
| UNC School of the Arts |
Fighting Pickle |
|
| UNC School of Science and Math |
Unicorn |
|
| Wake Forest University |
Demon Deacons |
|
| Warren Wilson College |
Owls |
|
| Western Carolina University |
Catamount |
“Paws” |
| Wingate University |
Bulldog |
|
| Winston-Salem State University |
Ram |
|
The Alamance County Public Libraries has just shared issues of the State Dispatch, later known as the Twice-a-Week Dispatch, on DigitalNC. Issues are available from 1908-1915 (with some exceptions).
The tagline of the Dispatch began as “A Republican newspaper devoted to the upbuilding of American homes and American industries,” and later changed to include the word “progressive.” The paper covers Republican events and ideas, as well as local news from Burlington and surrounding areas of Alamance county like Graham and Whitsett. Later issues see the beginnings of World War I.
This paper joins other Alamance county papers on DigitalNC: The Alamance Gleaner, the Mebane Leader, and the Elon University Student Newspaper. Alamance County Public Libraries has also shared additional items that can be found through their contributor page.
April Fool’s Day is upon us. (We thought Google Chrome’s support for emoji translation could be really useful for transcribing some of our newspapers!) These days it seems April Fool’s is mostly played out online, with websites jockeying for the best prank. Taking a look through DigitalNC’s Newspaper Collection shows that pulling pranks on April Fool’s via [print] media is nothing new.
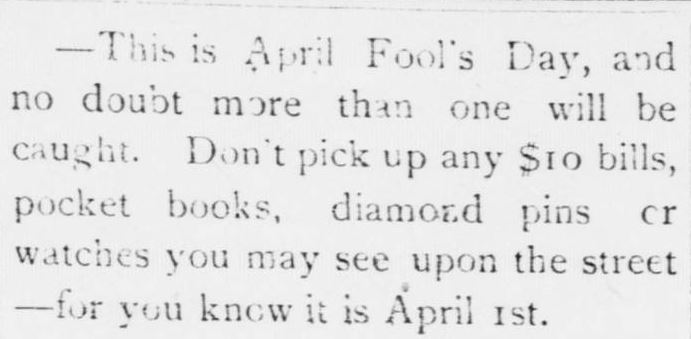
The oldest reference found to April Fool’s Day in the newspapers is from The Wilson Advance in 1897, which reminded its readers which day it was and to be on the alert for pranksters. The small news item gives a glimpse of what April Fool’s jokes entailed in the late 1890s. (for context, $10 in 1897 would equal approximately $268 today)

Starting with the 1937 April Fool’s Day issue of the Clarion from Brevard College, which is the first appearance of an April Fool’s themed paper in NC Newspapers, it appears that special April Fool’s Day editions of student newspapers were popular across North Carolina, as they remain today if you browse through some campus newspapers online. Some of the funnier news headers we found included a color by number of Elon’s Pendlelum in 1999 and the 1991 Goofordian [regularly the Guilfordian] from Guilford College, which also noted that you can read all about the debate over the sweatiest professor on page 2.


To view more newspapers from across North Carolina, visit the North Carolina Newspapers collection and to view specifically more papers from April 1 through the years, check out the “Today in North Carolina History” section on the right side of the page.

Thanks to our partner, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, a batch of fill-in issues of the Winston-Salem Chronicle spanning from 1975 to 2013 are now available on our website. Included among the issues added were February 7, 1985 and June 27, 1985. These particular issues are notable for their articles written on Darryl Hunt, a Black Winston-Salem man who was falsely convicted of murdering (among other charges) Deborah Sykes in 1985.
The Winston-Salem Chronicle staff was among the many community members that voiced their concerns over the arrest of Darryl Hunt. In the February 7, 1985 issue of the paper, executive editor Allen H. Johnson writes a large, three page article on the case, using every inch of the pages to humanize Hunt and point out the inconsistencies of the case.
In the article, Johnson includes several interviews from community members and organizations such as Alderman Larry Little, Hunt’s uncle William Johnson, and the NAACP. In these interviews, many community members mention their shock and vehement disbelief that Hunt could have committed murder. Even Hunt’s sixth grade teacher was interviewed, saying: “‘I cried like a baby because I knew he wasn’t guilty,’ […] I know that kid and there’s no way …. I’d bet my life on it that he isn’t capable of this horrendous crime.'”
Despite inconsistencies, lack of concrete evidence, and efforts by the community, Hunt was convicted and sentenced to life in prison on June 14, 1985. In 1989 however, the North Carolina Supreme Court overturned the previous conviction due to the original prosecutors introducing false statements made by Hunt’s at-the-time girlfriend which she recanted before the initial trial. On appeal, Hunt was released on bond and offered a plea bargain where he would be sentenced to the time he had already served (five years) for a guilty plea. Hunt rejected the bargain and went through a retrial. He was again convicted and sentenced to life in prison.
After the second conviction, Hunt’s attorneys Mark Rabil and Ben Dowling-Sendor filed for the DNA gathered from the crime scene to be tested. The results came back in October of 1994 and determined that the DNA did not match Hunt’s. Despite the results, requests for an appeal were rejected. The reasoning given for the denied appeal was that new evidence was not absolute proof that Hunt was not involved.
Ten years after learning that the DNA did not belong to Hunt, authorities ran the crime scene DNA through the state’s database. It was discovered that the DNA actually belonged to Willard E. Brown, a man who was already incarcerated for another murder. Finally, after serving 19 years in prison, Darryl Hunt was exonerated on February 6, 2004.
To read more issues of the Winston-Salem Chronicle, please click here.
To view more newspapers from across North Carolina, please click here.
To learn more about the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, please visit their website.
Information about the Darryl Hunt case was gathered from Phoebe Zerwick’s Beyond Innocence: The Life Sentence of Darryl Hunt, the Innocence Project, and DigitalNC graduate assistant Sophie Hollis.
Thanks to our partner, Western Carolina University, fourteen issues of Cullowhee High School’s yearbooks are now available on our website. This batch covers the years 1955-1957, 1960-1967, and 1969-1971.
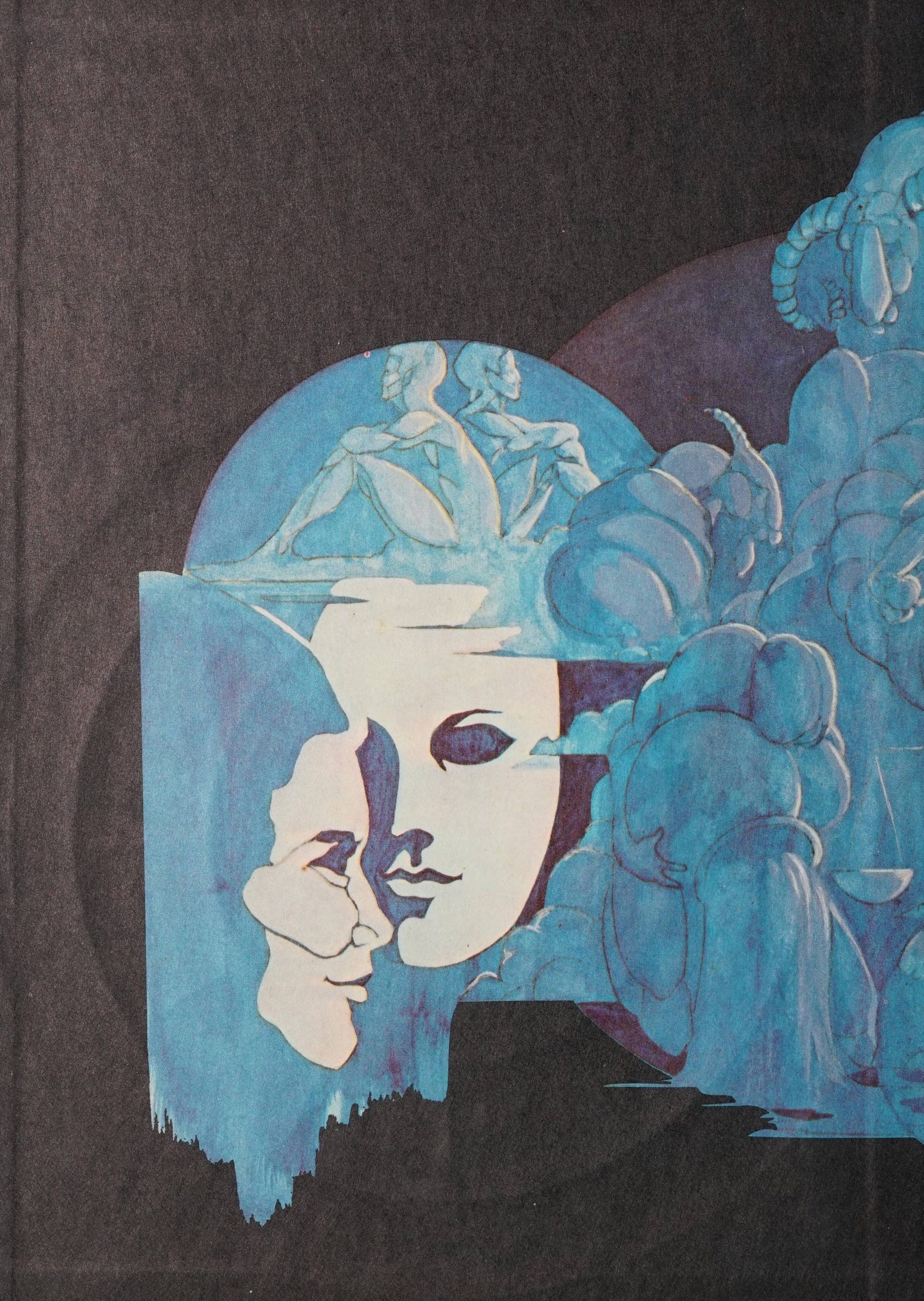
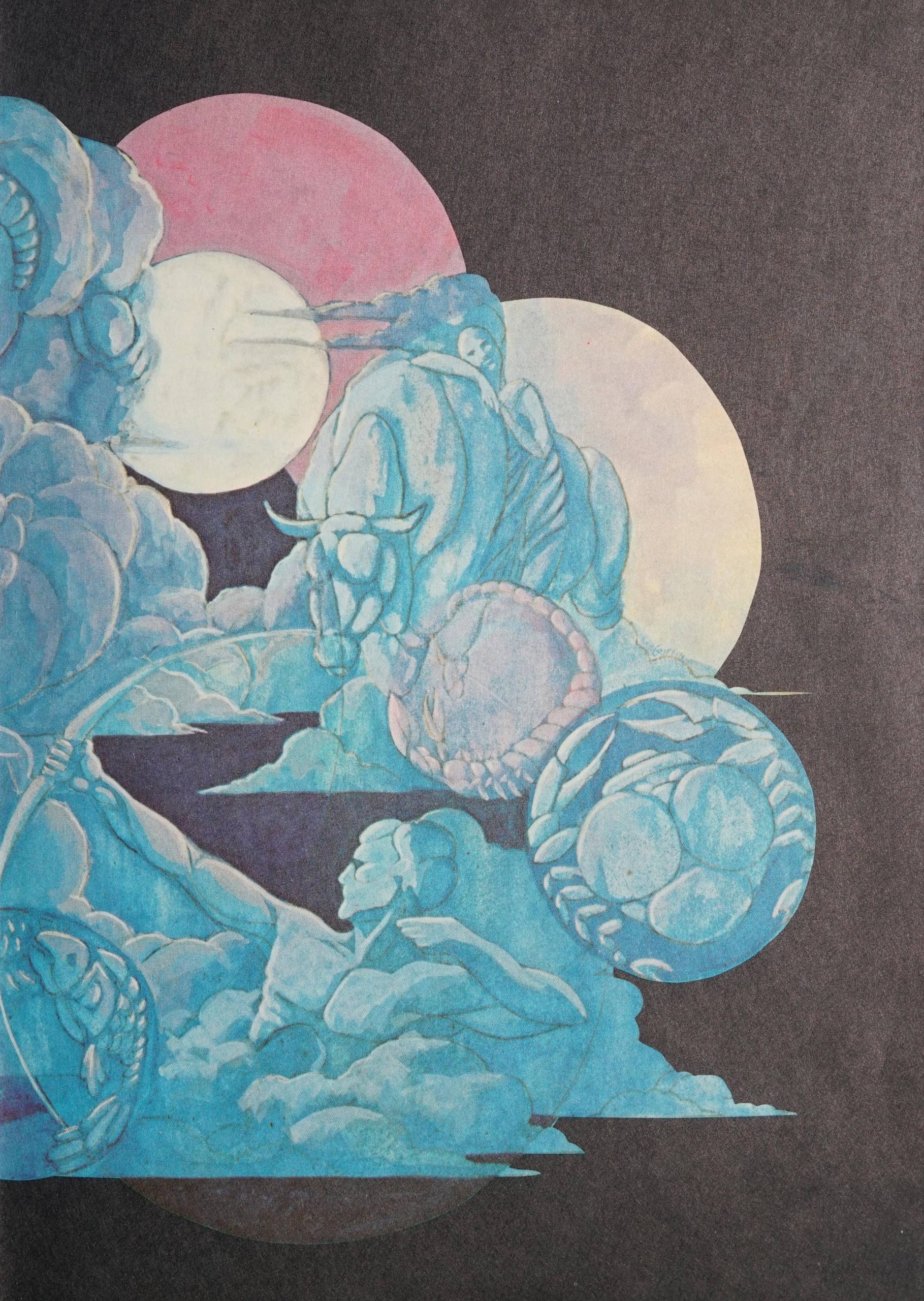


The 1970 Cullowhee High School yearbook from this batch is particularly interesting. The theme for the yearbook was astrology. In the first pages of the book there are two circles. The first informs the reader which of the zodiac they belong to. The second circle serves as a table of contents where each section of the book is represented by a different zodiac. For each zodiac, the contents of the section are laid out for the reader to easily navigate the yearbook. For example, in the “Virgo” section you will find the most school spirited, student council, and elementary school (seen in the picture below). After each zodiac section is introduced there is a page which contains pictures of students along with quotes that describe that zodiac’s traits. The yearbook also features front and back inside covers with a beautiful colored illustration of the various Western zodiacs which can be seen in the pictures above.
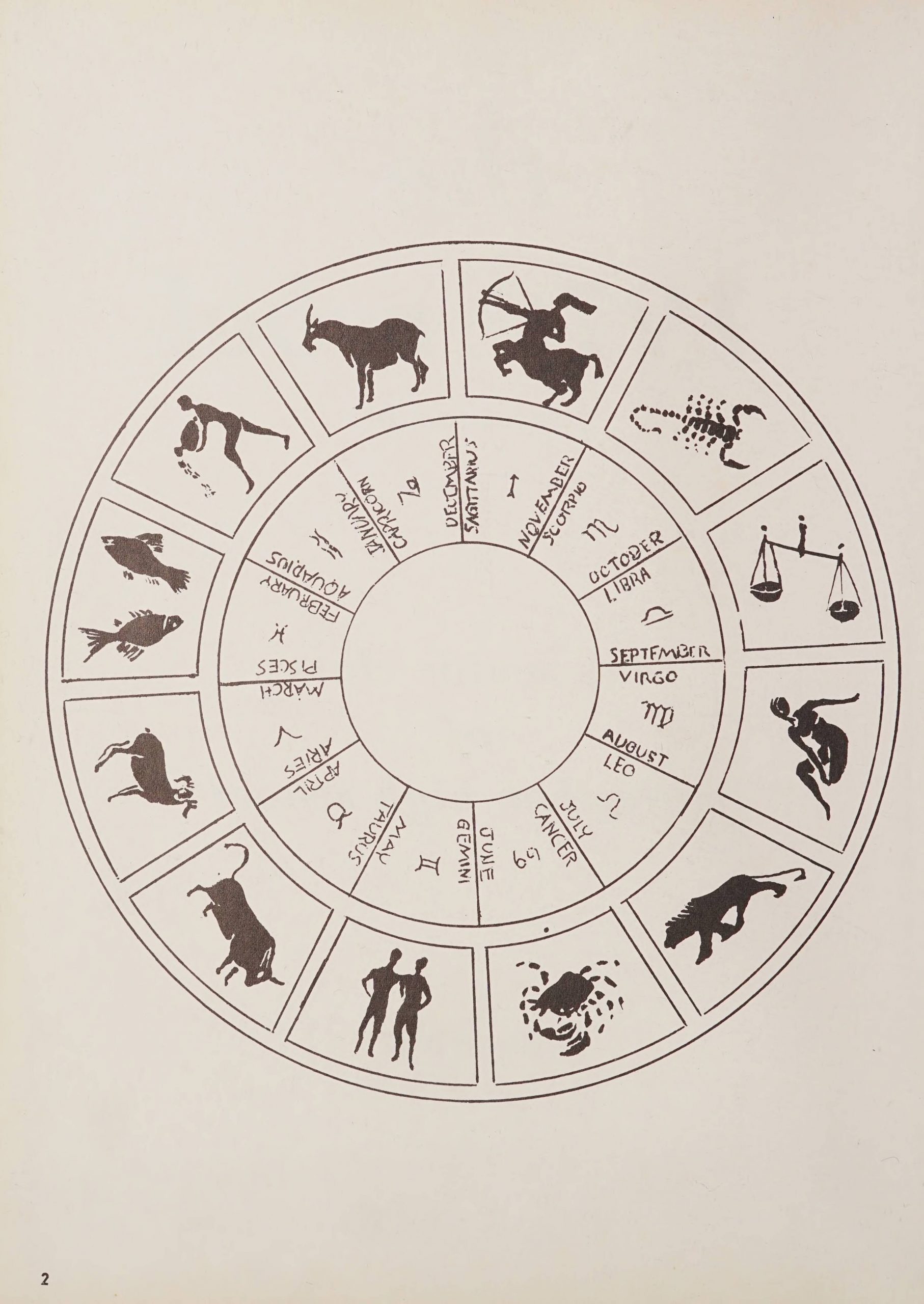
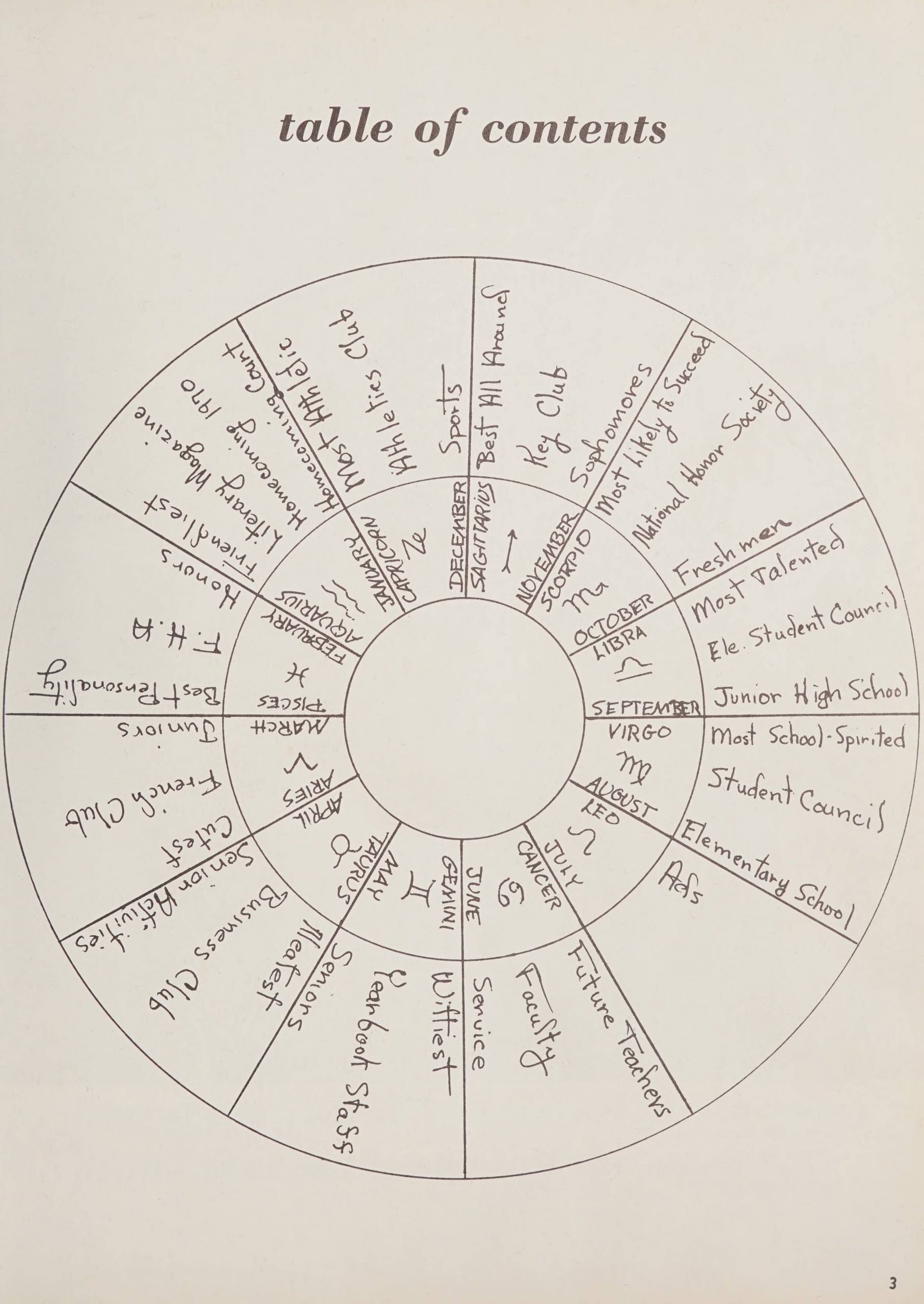
To learn more about Western Carolina University, please visit their website.
For more yearbooks from across North Carolina, visit our yearbook collection.

Page 31 of Annie Gordon Floyd’s scrapbook, a student at Elon College during the influenza pandemic of 1918. The newspaper clipping is Annie’s obitual; she died of influenza.
Here at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, as well as across the globe, graduating students are leaving their school years behind without the normal pomp and circumstance. After years of late-night study sessions and racing to beat the assignment submission clock on Sakai, who would have thought that a pandemic would get between them and their walk across the commencement stage? While achieving a degree is a reason to celebrate regardless of location, perhaps 2020 graduates and all self-isolating students can relate to the experiences of an older group of students- those affected by the 1918 influenza pandemic.
Cutting through the spring of 1918 to 1919, the influenza pandemic was a worldwide health issue not unlike today. In North Carolina, industries were halted and quarantine was enacted (and extended). Universities, too, established their own versions of quarantine. Thanks to the institutions we work with here at DigitalNC, we have digitized yearbooks, scrapbooks, and college publications that offer a glimpse into the thoughts of students during this equally tumultuous time in history.
Quarantine was enacted in fits and spurts on campuses across North Carolina between 1918 and 1920. As is evident by yearbook social calendars, measures varied across universities. One campus quarantined through most of November 1918 while others were still starting up quarantine periods in February and March 1920.
Campus clubs have a dedicated slice of yearbook real estate during this time and the influenza directly impacted their activities. As the pandemic coincided with the last days of World War I, Student Army Training Corps (S.A.T.C.) were a part of many universities. The S.A.T.C. at Meredith College recounts their quarantine movements that saved faculty and students from “nervous prostration”. UNC’s S.A.T.C. found the flu less inspiring. Other students responded by creating clubs. At Queens College, Quarantine Club, seen left, first began in 1918 with the aim “to extend the quarantine”. Later, in 1920, the club edited their name to simply “Flu” Club, as seen below.

“Flu” section of the Meredith News and Distributor by French Haynes, Oak Leaves, 1919.
Students also utilized their yearbooks to creatively vent frustrations. In 1918, Atlantic Christian College students were under quarantine from February 6th to the 27th. Student Bonita Wolff penned several poems for The Radiant, including “Quarantined”, shown above. Another funny quarantine themed poem can be found in the advertisement section of the 1920 edition of St. Mary’s Muse.
Meredith College graduate French Haynes embedded influenza jokes throughout the satirical Meredith News and Distributor, shown to the right. And in 1920, Elizabeth Gaskins spotted a deficiency in her local health care system, due in part to the influenza, and argued for the creation of a local hospital in the Greenville High School yearbook The Tau.
If anything, these yearbooks serve as a reminder that this moment is not permanent. Comparing pandemics may be apples to oranges, especially when one student called quarantine “an awful bore” in a college that was only under quarantine for a month at a time, but Mary Reed Buchanan, member of the 1919 graduating class of the women’s college Peace Institute, offers some perspective in the senior class history:
With the warm spring came the renewal of all our former pleasures. There were parties galore, and girls, will you ever forget those State College receptions? And do you remember those exciting basketball games and the serenades afterwards? The feeling of being well again and out of quarantine brightened every heart and lightened every burden.
Even though we may not be attending basketball games anytime soon, we can look to those who have gone through a pandemic before and know that life, including student life, continues on. And for those who are graduating, Mary Reed Buchanan, noted suffragette, has final words:
For a look at all of DigitalNCs college and high school yearbooks, click here. Or, to view all memorabilia including scrapbooks, click here.

In today’s blog post I offer a break from the current election year with a trip back to the 1968 presidential election. Looking at the political landscape of 1968 is like looking at an earlier but familiar view of the same neighborhood we’re in now. It’s issues resonate today: striving for social and racial equality, debates over America’s place on the world stage. The late 60s were boiling with the turmoil of the Civil Rights Era and the Vietnam War. 1968 alone saw the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. in early April and presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy in June.
In April 1968, Time magazine held a mock presidential primary at colleges and universities to take the temperature of young Americans during that election year. Dubbed “CHOICE 68,” the event was covered in many of the student newspapers that can be found on DigitalNC, and I wanted to see what this nation-wide event looked like here in North Carolina.
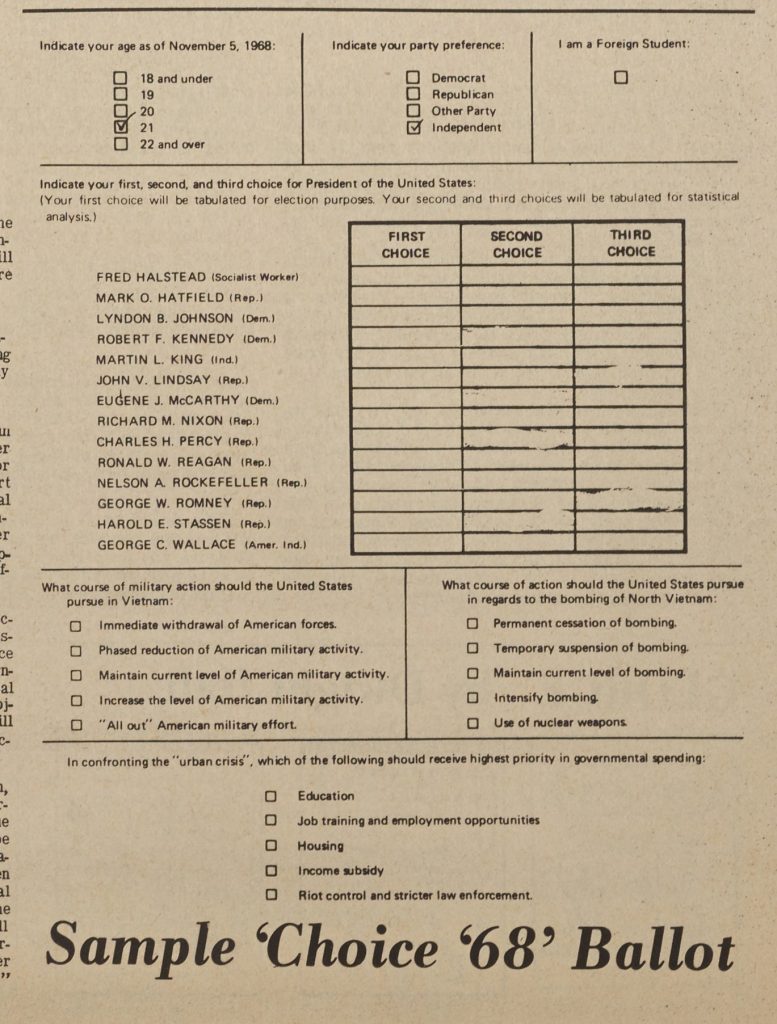
Sample Choice 68 Ballot, printed in Asheville-Biltmore College (now UNCA) newspaper The Ridgerunner, March 1, 1968.
Every American college and university was asked to participate in CHOICE 68. The event was governed by a group of eleven students representing a variety of campuses around the country. Campus groups were in charge of publicizing the event with their peers, under the direction of a campus coordinator. Each ballot (an early draft is shown at right) asked students to rank their top three choices for president and also asked for them to weigh in on Vietnam and the “urban crisis,” the latter of which referred to pervasive concern over poverty, crime, and general unrest in high population urban environments. Write-in candidates were also allowed. Votes from all campuses were tabulated by a UNIVAC computer in Washington, D.C. and the results were supposedly announced on television, with each school’s individual totals being returned during the first week of May.
Before the vote, student newspapers urged their readers to rally against apathy, to prove that young voters could impact the national arena. One Brevard College editorial called on moderates to vote, expressing frustration that liberal and conservative activists had been “hoarding the headlines.” An accompanying editorial talked about the conservatives still being committed to rooting out Communism, revealing lingering echoes of McCarthyism from the late 50s. It predicted a 1968 election win for then Governor of California, Ronald Reagan.
Campuses with active student government associations and/or political groups tended to have more events and publicity associated with CHOICE 68. North Carolina Wesleyan College’s student body listened to speeches in support of Senator Eugene McCarthy (D), former Vice President Richard Nixon (R), and current Vice President Hubert Humphrey (D), three of the most prominent contenders in early 1968. Voting booths, borrowed from the City of Rocky Mount, housed students punching out chads of computer cards to cast their votes.

Headline from the April 25, 1968 issue of The Twig, Meredith College.
Some schools had hundreds of participants, with 500 Elon students voting in the mock election. Others had fewer; thirty students were questioned at Meredith College. The Twig quoted opinions from four of those 30 (two Republicans and two Democrats) in the issue seen at right.
Salem College appears to have been one of the most enthusiastic participants, with articles about CHOICE 68 found in issues spanning January through May and a voter turnout of 73% of the eligible student body. The February 23 issue of The Salemite talked about how President Lyndon Johnson endorsed the national mock election despite the fact that “student dissent over the past year ha[d] been directed primarily against White House policies.” The April 12 issue asserted that “massive student participation in CHOICE 68 can and will affect the course of American politics in 1968.”
Almost all articles about the vote mentioned the UNIVAC computation of results, which was seen as heralding a new era in which computers could make generating results faster and more secure. The Meredith College Twig published a photo of the computer tabulating results in its April 25 issue (shown above). Dr. Hammer of UNIVAC posited a time when “a huge data bank may contain ‘voice prints’ of eligible voters” to authenticate those phoning in their votes (“A Letter from the Publisher,” Time, May 10, 1968, page 21).
Of the North Carolina schools* whose CHOICE 68 results I could locate, McCarthy came out on top for all except North Carolina State University, where Nixon prevailed and McCarthy came in second. Nixon was the second choice for 7 schools, and Nelson Rockefeller (R) carried second choice at the remaining 3.
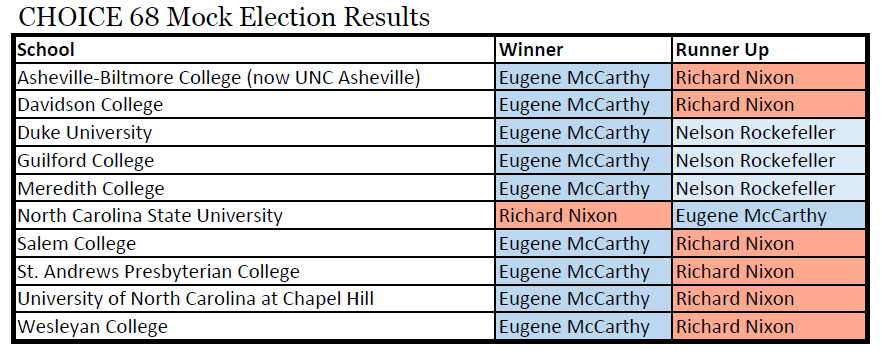
The national CHOICE 68 vote also saw McCarthy in the lead with 286,000 out of 1.7 million votes from 1,450 campuses. Robert Kennedy (D) and Nixon followed behind McCarthy. Students voted to reduce the United States military presence in Vietnam, and saw education as the biggest key to solving the “urban crisis.”
Though he won the CHOICE 68 vote and continued to be bolstered by student support through the primaries, McCarthy was beaten by Humphrey to gain the official Democratic nomination. The November election was won by Nixon, however the CHOICE 68 voters’ preference for a Democratic candidate was somewhat predictive: Humphrey prevailed with voters under 30 in the general election.
As far as I can tell, no nationwide poll quite like CHOICE 68 has been held since, though speculation over how college-aged Americans will vote certainly hasn’t changed. If you’re interested in other historical election news and opinion as reported by student newspapers, visit the North Carolina Newspapers collection.

November 5, 1968 issue of the Louisburg College Columns student newspaper. Students picked Nixon in a straw poll held close to the general election.
*It appears that the following schools also participated in CHOICE 68 based on mentions in newspapers and yearbooks, but no results were found: Appalachian State University, High Point College, Lees-McRae College, Lenoir-Rhyne College, Queens College, and University of North Carolina at Greensboro.

First page of the March 1979 issue of The Informer newsletter.
The Digital Heritage Center has worked with over 150 libraries throughout North Carolina. It’s no surprise that DigitalNC.org boasts a good number of items that document the history of libraries in the state, including scrapbooks and photos.*
For many years libraries were purposefully segregated, with branches tacitly or overtly meant to serve an African American neighborhood or community. The Richard B. Harrison Library in Raleigh is an example of a library that was a true social force, due to the hard work and influence of librarian Mollie Huston Lee. I thought of Ms. Lee recently. I was doing some work in our scrapbook collection, when I came upon an interesting newsletter tucked into one of the Irwin Holmes scrapbooks from the Durham County Library.
Titled “The Informer,” the newsletter’s tagline is: “For Recruitment of Minority Librarians” and appears to have been published first out of Raleigh and then out of Fort Valley, Georgia. There are two (possibly two and a half) issues in the scrapbook: one dating from March 1979 (pictured at right) and the second from September 1983. The issues of The Informer in our collection give biographies and moving tributes to African American librarians, such as Ann M. Jenkins of NCCU and Edna “Pinky” Penolya Mcaden King Watkins, an NCCU graduate who worked in libraries around the country. They also list positions available in North Carolina and around the country. The Informer publisher, IESMP or “Information Exchange System for Minority Personnel,” sold a number of other publications that offered to help librarians find jobs at institutions friendly to hiring minorities.
Dr. Dorothy May Haith was The Informer’s editor and possibly publisher, and she has had a lifelong passion for improving the profession and her community. A Shaw University and North Carolina Central University alum (she also holds degrees from Indiana University), Haith led the library at Bennett College, and also at Howard University. She has a number of publications to her name, has served on professional boards, and has given back to educational institutions by endowing scholarships. The Spring 2011 issue of Windows, published by the University Library at UNC Chapel Hill, describes a gift made to Wilson Library by Haith to honor those she felt encouraged her education (we call Wilson Library our home).

Dorothy Haith’s high school yearbook photo from Booker T. Washington High in Reidsville, N.C.
Through The Informer, Haith was building a network for minority librarians through the 1970s and 1980s, offering them professional resources and personal information about their peers. Though Googling gives most of us this benefit now (as it did for me when trying to find out more about Haith), before the internet, this was a true labor and a valuable service.
Recruitment of minorities and increasing diversity continues to be a great need. What many patrons may not realize is that libraries strive to be some of the most inclusive, safe spaces in the country. Many build towards that goal in numerous ways: through concerted efforts to recruit a diverse workforce, through selection of an inclusive and various group of materials for collections, and through ensuring libraries are safe for ALL patrons. In fact, the American Library Association, the national professional organization for librarians, reinforces these goals through a code of ethics, professional development, and scholarships. As a profession, we have a long way to go, but these steps get us closer.
At DigitalNC, we hope to identify and help share more collections from our partners related to North Carolina’s minority populations in the coming year. If you work at a library or other cultural heritage institution and have collections that fit this category that you’d like to share online, we’re eager to hear from you.
*There’s also a rich Library History digital collection from the State Library of North Carolina.
**NCCU has numerous issues of The Informer in their collection, available at the School of Library and Information Sciences Library.
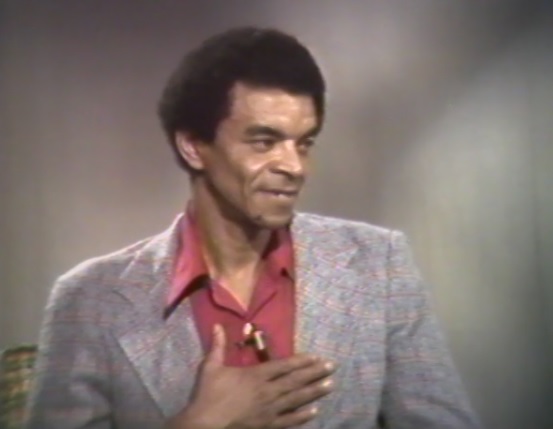

Yusuf Salim interviewed for Durham Technical Institute and Arts in Durham.
From Durham Technical Institute’s Community Video Services and the Durham Arts Council, Cynthia Watts interviews Yusuf Salim in Arts in Durham, Brother Yusuf, 1979. This moving image can be found in DigitalNC’s new North Carolina Sites and Sounds Collection. It was contributed by the Durham Public Library.
Born Joseph Blair in Baltimore in 1929, Yusuf Salim was a lifelong Jazz pianist and composer, performing in several bands in Baltimore, New York City, and Durham. Salim was a well-known figure in Durham, but apart from his small collection of archival material, his memory now resides mainly in the hearts of Durhamites who knew him. He served as a resource for the growing jazz community and often helped and hosted musicians who were settling in or passing through the Triangle. He was also known as a humanitarian and community activist, promoting peace among the rapidly diversifying population in the Triangle.
In the film, Watts askes Salim “Why did you choose Durham?” (3:14)
“Durham chose me.” Salim continued to describe his love of the Triangle area. He discussed the many “points of reference” by which he compared his experience. One such moment was his time as a Marine in Eastern North Carolina. Even in his full Marine uniform he was forced to walk in the dirt to let white people pass. But times had changed in the Triangle and Salim’s attitude and outlook were positive, which he credits to his Islamic faith. Salim also spoke openly about his struggle with heroin and how his faith freed him from his addiction. He went cold-turkey upon his move to Durham in 1974 and was clean from then on.
More than half of the moving image is dedicated to what Salim did best– jazz performance. The film documents 15 minutes of Salim’s skill on the jazz piano.
Two other moving image items from the the Durham Public Library that also feature Salim are available on DigitalNC:
Salim died in 2008 after a battle with prostate cancer. His memorial was held at the Hayti Heritage Center in Durham. This moving image offers a warm memory of a beloved Durham jazz icon and captures a moment of the art scene in the Triangle during the 1970’s. For more information and research about Yusuf Salim and his life in Durham, please visit Duke University’s Rubenstein Library where his collection is housed. It holds many of the original scores that he composed. Related material about Jazz in Durham can be found at the Durham Main Library in the Bus Brown Collection. You can also view many other materials shared by Durham County Library on DigitalNC or in their own digital collections.